Routing and Wavelength Assignment in Optical WDM Networks
The Routing and Wavelength Assignment Problem in Optical WDM Networks tackled under a MultiObjective (MO) approach
Coordinator/contact:
- Esta dirección electrónica esta protegida contra spam bots. Necesita activar JavaScript para visualizarla
- Esta dirección electrónica esta protegida contra spam bots. Necesita activar JavaScript para visualizarla
Introduction
The technology based on optical fiber enables transmitting information from one device to another by sending pulses of light through an optical fiber. This technology has revolutionized the telecommunications industry.
The most promising technology to take full advantage of the bandwidth of the optical networks is based on Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM). This technique multiplies the available capacity of an optical fiber by adding new channels, each channel on a new wavelength of light. This approach ensures fluent communications between different devices interconnected by a specific optical network. Therefore these devices are able to send and receive information without bottlenecks. When it is necessary to interconnect a set of source-destination paths a problem comes up, this problem is known as Routing and Wavelength Assignment (RWA). In this problem is required to fulfill the next two constraints:
- Wavelength conflict constraint: A wavelength may be used only once per fiber at a given instant.
- Wavelength continuity constraint: If a wavelength conversion is not possible, a lightpath must be assigned the same wavelength along its route from the source node to the destination node.
This problem is known as Routing and Wavelength Assignment (RWA) and there are two types, Static-RWA and Dynamic-RWA. In Static-RWA the set of lightpaths are given in advance, so the problem consists of finding a solution that minimizes network resources used. On the other hand, in Dynamic-RWA, the lighthpaths must be established in real-time. In this case, if a lightpath request does not find a route with free wavelength, a deadlock is presented. Both types, static and dynamic RWA, are NP-complete problems, therefore it is very common the use of heuristic techniques to solve them.
Routing and Wavelength Assignment Problem (RWA)
An optical network is modeled as a direct graph G=(V,E,C), where V is the set of nodes, E is the set of links between nodes and C is the set of available wavelengths for each optical link in E.
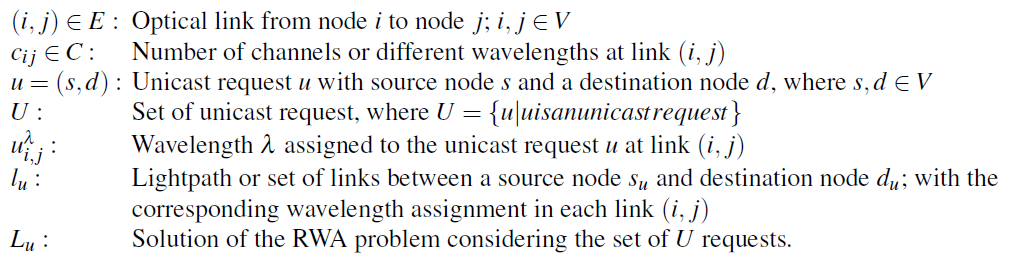
Notice that 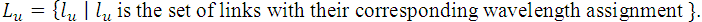
Using the above definitions, the RWA problem may be stated as a Multiobjective Optimization Problem (MOP) , searching the best solution that simultaneously minimizes the following two objective functions:
- Hop Count (y1):
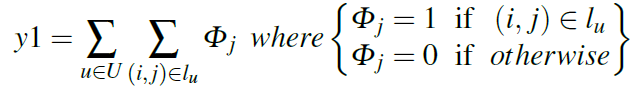
- Number of wavelength conversions (y2):
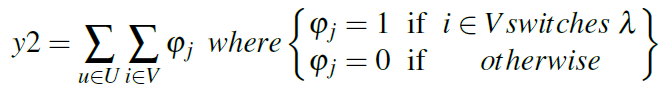
An example helps to understand the formulation problem and the objective functions of RWA problem, presented above.
Statement: Given the optical network topology of Fig.1, suppose the next set of five lightpaths and number of different wavelengths at link:
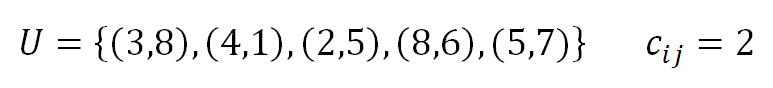
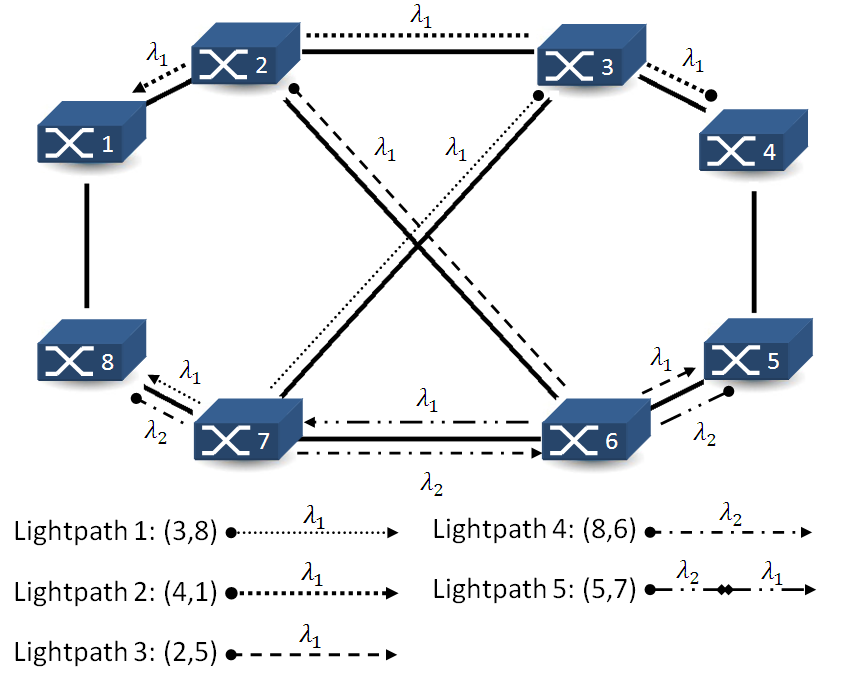
Fig. 1. Possible solution for the Example
As we can see in Fig.1, the lightpath requests 1, 2, 3 and 4 do not present any wavelength switching; however, the lightpath 5 presents one wavelength conversion.
In Table 1, we present all necessary calculations to obtain the value of the two objective functions, hops (y1) and wavelength switching (y2). The solution presented for this specific topology could not be the best one; this example only tries to help to understand the problem formulation and the objective functions.
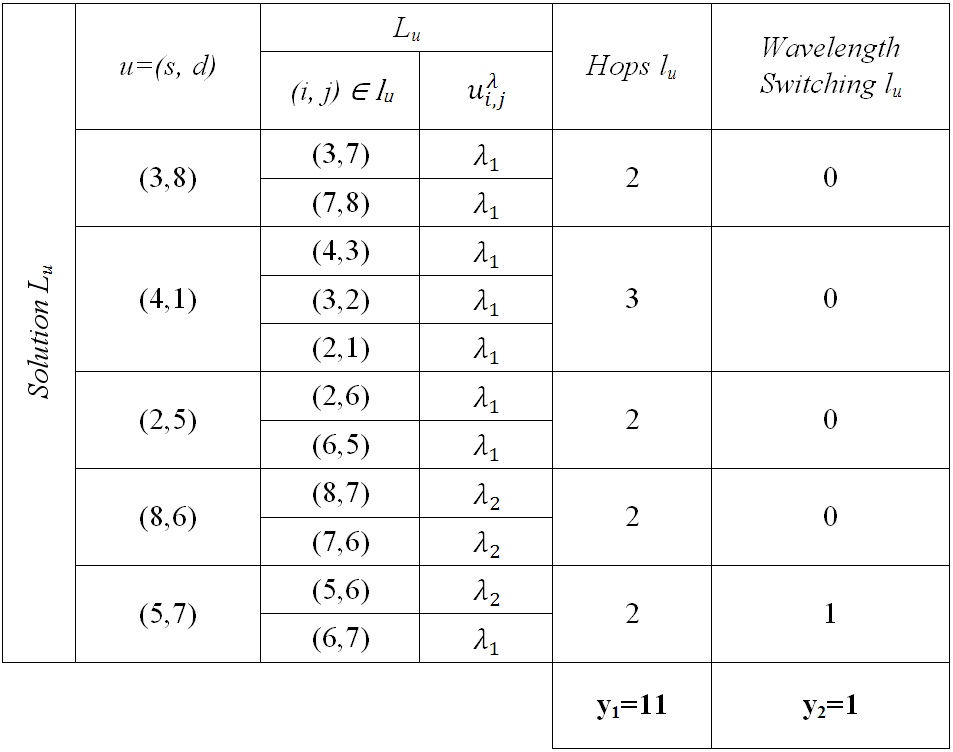
Table 1. Calculations to obtain objective functions in Example
Instances
Obtain here some of the instances used in our research.
References
- "Using a Multiobjective OpenMP+MPI DE for the Static RWA Problem", in: "Computer Aided Systems Theory, LNCS, Vol. 6927" . Álvaro Rubio-Largo, Miguel A. Vega-Rodríguez, Juan A. Gómez-Pulido, Juan M. Sánchez-Pérez. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2012, pag:224-231. ISBN:978-3-642-27548-7.
- "A Multiobjective Gravitational Search Algorithm Applied to the Static Routing and Wavelength Assignment Problem", in: "Applications of Evolutionary Computation. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 6625" . Álvaro Rubio Largo, Miguel A. Vega-Rodríguez, Juan A. Gómez Pulido, Juan M. Sánchez Pérez. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2011, pag:41-50. ISBN:978-3-642-20519-4.
- "Tackling the Static RWA Problem by Using a Multiobjective Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm", in: "Advances in Computational Intelligence. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 6692" . Alvaro Rubio-Largo, Miguel A. Vega-Rodríguez, Juan A. Gómez-Pulido, Juan M. Sánchez-Pérez. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2011, pag:364-371. ISBN:978-3-642-21497-4.
- "A Hybrid OpenMP/MPI Differential Evolution for Solving the RWA Problem". Alvaro Rubio-Largo, Miguel A. Vega-Rodríguez, Juan A. Gómez-Pulido, Juan M. Sánchez-Pérez. Computer Aided Systems Theory - Extended Abstracts, A. Quesada, J.C. Rodriguez, R. Moreno jr., R. Moreno (Eds.). IUCTC. Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, 2011, pag:236-238. ISBN:978-84-693-9560-8.
- "Improving Optical WDM Networks by using a Multi-core version of Differential Evolution with Pareto Tournaments", in: "Distributed Computing and Artificial Intelligence" . Álvaro Rubio-Largo, Miguel A. Vega-Rodríguez, Juan A. Gómez-Pulido, Juan M. Sánchez-Pérez. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2010, pag:629-636. ISBN:978-3-642-14882-8.
- "Solving the Routing and Wavelength Assignment Problem in WDM Networks by using a Multiobjective Variable Neighborhood Search Algorithm", in: "Soft Computing Models in Industrial and Environmental Applications. Advances in Intelligent and Soft Computing, vol. 73" . Alvaro Rubio-Largo, Miguel A. Vega-Rodríguez, Juan A. Gómez-Pulido, Juan M. Sánchez-Pérez. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, Germany, 2010, pag:47-54. ISBN:978-3-642-13160-8.
- "A Differential Evolution with Pareto Tournaments for solving the Routing and Wavelength Assignment Problem in WDM Networks". Alvaro Rubio-Largo, Miguel A. Vega-Rodriguez, Juan A. Gomez-Pulido, Juan M. Sanchez-Perez. Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC 2010), IEEE Computer Society, Barcelona, Spain, 2010, pag:129-136. ISBN:978-1-4244-6910-9.
 Problems
Problems